Annual Audit and Compliance in China
A handy step-by-step walk through on how to prepare an annual audit or 'health check' on your business. Who could say no?
Here's our summary of the report...
Annual Audit and Compliance in China
According to China’s company law and other relevant regulations, all Foreign Invested Enterprises (FIEs) in China are required to follow the annual audit and other compliance processes. FIEs included are:
- Wholly Foreign Owned Enterprises (WFOEs)
- Joint Ventures (JVs)
- Foreign Invested Commercial Companies (FICEs)
- Representative Offices (ROs).
Why is the annual audit important for FIE’s in China?
FIEs can only distribute and repatriate their profits or dividends back to their home country after completing their annual audits and settling all relevant tax liabilities. Failure to comply with the annual audit and related measures may result in extra expenses, penalties, or even revocation of business licenses.
Why should you start your annual audit early?
Preparing your annual audit is time consuming and the Chinese tax bureau takes the deadline seriously, companies that are not able to hand in the audit report on time will face fines. Furthermore, according to Company law of the PRC, the annual compliance review has to be done by a Certified Public Accountant (CPA) in order to ensure the compliance to all tax regulations.
Whilst most FIE’s start typically start preparing for the audit in January, tax advisors suggest FIE’S should start the process as early as November or December.
Annual Compliance Timeline
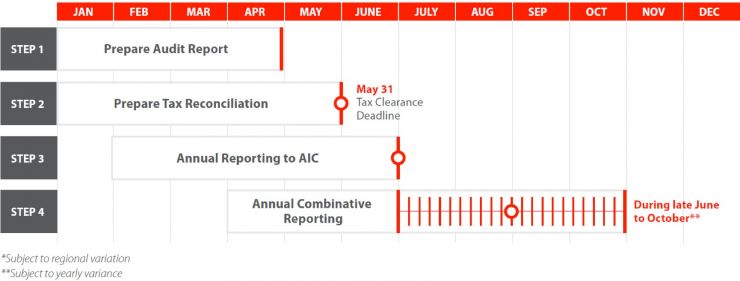
What are the key areas in an annual audit?
For WFOEs, JVs, FICEs, purchases and sales are usually the most vulnerable areas in an annual audit. This means more time should be spent ensuring that the accounting data is genuine and accurate. This should be done by comparing transactions with the corresponding contracts, invoices, orders and inventory changes..
For ROs, as they usually have relatively simple business operations, more attention should be paid to expense accounts and financial statements.
Six ways companies can prepare for the annual audit
1.Check if your company utilized all tax and fee reductions
This is especially important in 2018 as the state government implemented a number of tax and fee reduction policies to support businesses operating within China. For example, the Corporate Income Tax (CIT) law to support small and low profit enterprises.
2.Check if the expense deduction caps were reached
According to CIT law, reasonable expenditure incurred in relation to income received by an enterprise can be deducted from gross income.
This usually includes:
- Costs, expenses, taxes (except CIT and VAT) and losses
- Reasonable depreciation of fixed assets
- Amortization of intangible assets
- Amortization of long-term prepaid expenses
- Inventory cost
- Net-value of an asset transferred
- Donation expenditure according to relevant regulations.
It is necessary to examine large expenses or capital expenditures and conduct a comprehensive review of the depreciation of fixed assets and amortization of intangible assets.
4. Check whether pre-tax deduction vouchers are in compliance
Pre-tax deduction vouchers refer to various proofs used by an enterprise when computing taxable income for Corporate Income Tax Incentive (CIT) purposes. This pre-tax exercise helps prove that the reasonable expenditure related to income was actually incurred.
5. Check accuracy of additional R&D expense deductions
To encourage innovation, the CIT law stipulates that qualified resident companies in China can enjoy pre-tax additional deductions based on their research and development (R&D) expenditures.
6. Check whether documents for CIT incentives are prepared
According to “Measures on Handling of Corporate Income Tax Incentives” (Revision 2018), enterprises can judge whether they are qualified to enjoy the CIT incentives. Incentives can be enjoyed when companies make CIT returns and retain relevant documents for potential inspection from the tax bureaus.
Important Dates
- 31 May - Deadline to submit CIT Reconciliation Report & Tax reconciliation deadline (the audit procedure takes about two months, so the audit report should be prepared before the end of April)
- 30 June - Deadline to submit Annual Report to AIC*
- 30 June - Deadline to submit Annual Combinative Report*
*subject to locality and yearly variance
Preparing an annual audit is a good chance to perform a “health check” for your company. The audit will reveal your company’s performance and help analyze your internal structures performances on cost and tax efficiency.
To read the whole report written by Dezan Shira & Associates, click here






